Indexed In
- Academic Journals Database
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- Academic Keys
- JournalTOCs
- China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI)
- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
- Electronic Journals Library
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- SWB online catalog
- Virtual Library of Biology (vifabio)
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
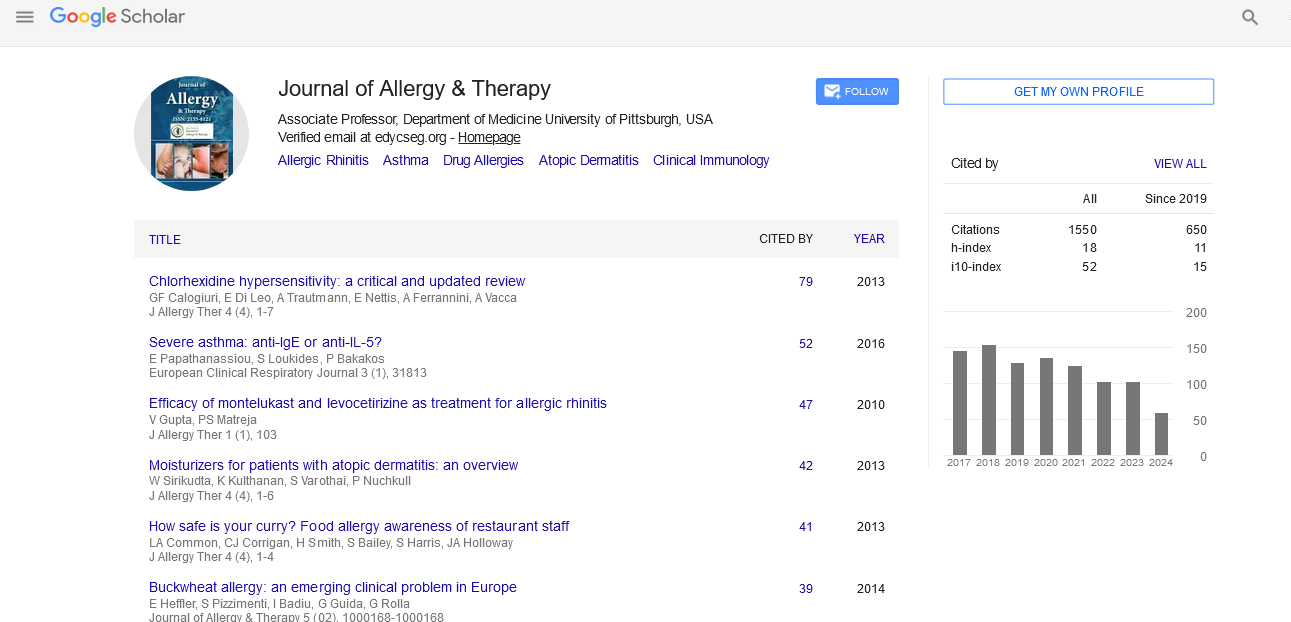
The use of Pichia pastoris in the production of recombinant proteins for the diagnosis of allergic diseases
7th International Conference on Allergy, Asthma and Clinical Immunology
September 14-15, 2016 Amsterdam, Netherlands
Lahiani Sadjia and Moreno Galleni
University Mâ??Hamed Bougara de Boumerdès, Algeria
Université de Liège, Belgium
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Allergy Ther
Abstract:
Allergic diseases are a major public health problem. Respiratory allergies, mainly allergic rhinitis, asthma and allergic dermatitis are the most common manifestations. Allergy to house dust mites is the most common cause of asthma and allergic rhinitis. Our goal is to determine the prevalence of group 5 allergens from Dermatophagoides ptyronyssinus (Der p 5) and from Blomia tropicalis (Blo t 5), Recombinant proteins produced by the use of Pichia pasturis. DNA encoding these proteins has been cloned into cloning and expression vectors, expressed in Pichia pastoris SMD 1168. Both allergens Der p r 5 and r Blo t 5 were purified, characterized by mass spectrometry and circular dichroism. IgE reactivity was measured by means of indirect ELISA tested to measure specific IgE levels in sera of 64 asthmatic patients. The results obtained by circular dichroism show that rDer p 5 and rBlo t 5 are helical protein with a predominance of alpha-helical secondary structure. By mass spectrometry it was demonstrated that these two allergens are monomeric under physiological conditions. The recognition rate of rDer p 5 and t 5 rBlo by specific IgE asthmatic patients is 28% and 6%, respectively; the results obtained by indirect ELISA showed that these two proteins pose no cross-reactivity between them. Both species of mite, Dermatophagoides ptyronyssinus and Blomia tropicalis are answered in Algeria, class 5 recombinant proteins of these two species can be used for the diagnosis of allergic diseases and specific immunotherapy.
Biography :
Email: slahiani@student.ulg.ac.be