Indexed In
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- Academic Keys
- JournalTOCs
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- SWB online catalog
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Short Communication - (2022) Volume 11, Issue 2
Possible Relationship between Zonulin, Metformin and Insulin Resistance in Polycystic Ovarian Women
Manal Abdulmunem Ibrahim*Received: 28-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. PDS-21-13605; Editor assigned: 03-Mar-2022, Pre QC No. PDS-21-13605 (PQ); Reviewed: 17-Mar-2022, QC No. PDS-21-13605; Revised: 24-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. PDS-21-13605 (R); Published: 31-Mar-2022, DOI: 10.35248/2167-1052.22.11.265
Abstract
Zonulin protein is important to increase gut permeability, and its level is correlated with insulin resistance in polycystic ovarian women. Also, estrogen level is correlated with serum zonulin. Metformin, an insulin sensitizing drug can decrease serum zonulin in those patients. It is important to do new researches to know the mechanism of hormonal, and metformin effects on zonulin.
Keywords
Zonulin protein; Metformin; Gut permeability
Description
Zonulin is a haptoglobin precursor protein modulates the permeability of tight junction between cells of the digestive tract [1,2]. The increase of zonulin is associated with an increase in gut permeability; therefore Zonulin is suggested to have a role in the production of metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance [3]. Features of insulin resistance, sex hormone imbalance and infertility that accompanied polycystic ovarian syndrome which affect 3%-10% of women during their reproductive age [4-7], may be related to Zonulin level, as Zonulin is correlated with insulin resistance in those patients [8]. Moreover, irritable bowel syndrome and chronic fatigue syndrome, two conditions common in PCOS are linked to an increase in gut permeability [9,10]. The insulin-sensitizing drug, metformin that has many beneficial effects for polycystic ovarian patients may play a role in gut permeability due to its effect on gut microbiota by inhibition of bacterial complex I in a similar manner to metformin action on mammalian cell [11] or by another mechanism. We try to find if metformin has an effect on zonulin level.
It is found that 50% of metformin remain unabsorbed and retained in gut mucosa at 30-300 concentration folds than plasma concentration [12]. Metformin can delay absorption of glucose from intestine and increase production of Glucagon Like Peptide [13,14], and increase microbiota that produce short chain fatty acid that is important for insulin sensitivity [15,16], in addition to its insulin sensitizing effect in other tissue of the body [17,18].
Insulin resistance can be measured by different techniques, the most suitable non-invasion technique is measurement of homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), HOMA-IR=fasting insulin × fasting glucose divided by 22.5 [19-21]. A recent study for polycystic ovarian women showed that patients with (HOMA-IR) less than 2, exhibit no significant decreases in insulin and zonulin after three months of 850 mg metformin twice daily (Table 1), while polycystic ovarian women with HOMA-IR between 2 to 4 showed significant decrease in zonulin level p=0.01 and significant decrease in insulin level p=0.04 after three months of metformin treatment (Table 2), suggesting that metformin can decrease zonulin in insulin resistant patients only [22].
| Mean+SD | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting insulin (uIU/ml) | Before | 4.29+2.72 | 0.15 |
| After | 9.13+10.11 | ||
| Fasting glucose (mg/dl) | Before | 89.63+11.86 | 0.27 |
| After | 95.33+13.66 | ||
| HOMA-IR | Before | 0.96+0.62 | 0.13 |
| After | 2.43+2.93 | ||
| Serum zonulin (ng/ml) | Before | 20.83+15.46 | 0.52 |
| After | 16.90+15.21 | ||
Table 1: Statistical analysis before and after metformin therapy in polycystic ovarian women with initial HOMA-IR<2.
| Mean+SD | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting insulin(uIU/ml) | Before | 12.74+4.29 | 0.04* |
| After | 8.7+5.33 | ||
| Fasting glucose (mg/dl) | Before | 89.73+24.2 | 0.06 |
| After | 82.91+8.37 | ||
| HOMA-IR | Before | 2.8+0.93 | 0.02* |
| After | 1.79+1.17 | ||
| Serum zonulin (ng/ml) | Before | 16.26+10.10 | 0.01* |
| After | 7.92+5.09 | ||
Note: *p-value less than 0.05.
Table 2: Statistical analysis before and after metformin therapy in polycystic ovarian women with initial HOMA-IR=2 to 4.
However, Cetin suggested that insulin resistance is not triggered if there is integrity in gut permeability [23], while, Moghetti et al. revealed that metformin responders usually had higher fasting insulin [24]. The involvement of hormonal effect on zonulin and tight junction was approved by Zhou et al. study when they found that oestrogen has an inhibitory effect on certain protein expression important to strength tight junction [25], also according to another study, oestrogen showed a direct association with zonulin level in newly diagnosed polycystic ovarian women before starting metformin treatment (Figure 1) [26], which may be explained by that estradiol can decrease expression of protein zo-1 in tight junction and increase gut permeability leading to increase entrance of pathogen and giving rise to inflammation and expression of Interleukin 6 (IL-6), the latter can trigger more zonulin expression [27]. On the other hand, an another study showed that progesterone can decrease gut permeability by upregulating occludin protein an important protein in the structure of tight junction [28]. Recently, Ahmadi et al. find that metformin can treat aging-related leaky gut and inflammation, especially in obese individuals and people with high fat diet by beneficially modulating gut microbiome [29].
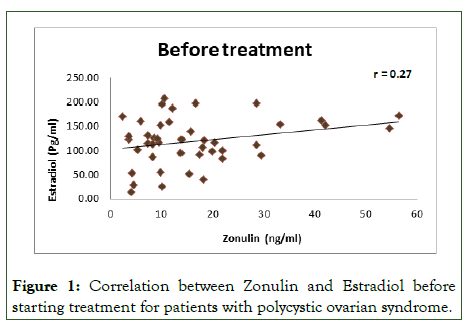
Figure 1: Correlation between Zonulin and Estradiol before starting treatment for patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Conclusion
Metformin can decrease serum zonulin level may be due to its effect on microbiome or to its effect on oestrogen level or its enhancement of ovulation and progesterone production that strength tight junction, or by another undiscovered mechanism. Further studies are required to find possible mechanism of hormonal and drug effect on tight junction and zonulin in polycystic ovarian women and other people due to the greatest importance for gut permeability in enhancement of insulin resistance and initiation of chains of sequences for appearance of complication of this syndrome.
REFERENCES
- Rittirsch D, Flierl MA, Nadeau BA, Day DE, Huber-Lang MS, Grailer JJ, et al. Zonulin as prehaptoglobin2 regulates lung permeability and activates the complement system. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013;304(12):L863-L872.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Pacifico L, Bonci E, Marandola L, Romaggioli S, Bascetta S, Chiesa C. Increased circulating zonulin in children with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(45):17107-17114.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Moreno-Navarrete JM, Sabater M, Ortega F, Ricart W, Fernandez-Real JM. Circulating zonulin, a marker of intestinal permeability, is increased in association with obesity-associated insulin resistance. PloS One. 2012;7(5):e37160.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Kauffman RP, Baker VM, DiMarino P, Gimpel T, Castracane VD. Polycystic ovarian syndrome and insulin resistance in white and Mexican American women: a comparison of two distinct populations. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;187(5):1362-1369.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Okoroh EM, Hooper WC, Atrash HK, Yusuf HR, Boulet SL. Prevalence of polycystic ovary syndrome among the privately insured, United States, 2003-2008. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2012;207(4):299.e1-299.e7.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- March WA, Moore VM, Willson KJ, Phillips DI, Norman RJ, Davies MJ. The prevalence of polycystic ovary syndrome in a community sample assessed under contrasting diagnostic criteria. Hum Reprod. 2010;25(2):544-551.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Azziz R, Carmina E, Dewailly D, Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Escobar-Morreale HF, Futterweit W, et al. The androgen excess and PCOS Society criteria for the polycystic ovary syndrome: The complete task force report. Fertil Steril. 2009;91(2):456-488.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Zhang D, Zhang L, Yue F, Zheng Y, Russell R. Serum zonulin is elevated in women with polycystic ovary syndrome and correlates with insulin resistance and severity of anovulation. Eur J Endocrinol. 2015;172(1):29-36.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Mathur R, Ko A, Hwang LJ, Low K, Azziz R, Pimentel M. Polycystic ovary syndrome is associated with an increased prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55(4):1085-1089.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Harlow B, Signorello L, Hall J, Dailey C, Komaroff A. Reproductive correlates of chronic fatigue syndrome. Am J Med. 1998;105(3):94S-99S.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Bridges HR, Jones AJ, Pollak MN, Hirst J. Effects of metformin and other biguanides on oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria. Biochem J. 2014;462(3):475-487.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Bailey CJ, Wilcock C, Scarpello JH. Metformin and the intestine. Diabetologia. 2008;51(8):1552-1553.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Bahne E, Hansen M, Brønden A, Sonne DP, Vilsbøll T, Knop FK. Involvement of glucagon‐like peptide‐1 in the glucose‐lowering effect of metformin. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016;18(10):955-961.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- McCreight LJ, Bailey CJ, Pearson ER. Metformin and the gastrointestinal tract. Diabetologia. 2016;59(3):426-435.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Pascale A, Marchesi N, Marelli C, Coppola A, Luzi L, Govoni S, et al. Microbiota and metabolic diseases. Endocrine. 2018;61(3):357-371.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Chambers ES, Preston T, Frost G, Morrison DJ. Role of gut microbiota-generated short-chain fatty acids in metabolic and cardiovascular health. Curr Nutr Rep. 2018;7(4):198-206.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Christakou CD, Kandaraki E, Economou FN. Metformin: An old medication of new fashion: Evolving new molecular mechanisms and clinical implications in polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol. 2010;162(2):193.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Xu H, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Ping J, Shou Q, Chen F, et al. Metformin improves hepatic IRS2/PI3K/Akt signaling in insulin-resistant rats of NASH and cirrhosis. J Endocrinol. 2016;229(2):133-144.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(6):1487-1495.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28(7):412-419.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Wongwananuruk T, Rattanachaiyanont M, Leerasiri P, Indhavivadhana S, Techatraisak K, Angsuwathana S, et al. The usefulness of homeostatic measurement assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) for detection of glucose intolerance in Thai women of reproductive age with polycystic ovary syndrome. Int J Endocrinol. 2012;2012:571035.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Ibrahim M, Ahmeid M. Metformin effects on zonulin level in polycystic ovarian women. ADMET DMPK. 2021;9(1):49-55.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Cetin Z, Kosem A, Can B, Baser O, Catak M, Turhan T, et al. Serum zonulin level is not elevated in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome without metabolic syndrome. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2019;300(6):1785-1790.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Moghetti P, Castello R, Negri C, Tosi F, Perrone F, Caputo M, et al. Metformin effects on clinical features, endocrine and metabolic profiles, and insulin sensitivity in polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 6-month trial, followed by open, long-term clinical evaluation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(1):139-146.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Zhou Z, Zhang L, Ding M, Luo Z, Yuan S, Bansal MB, et al. Estrogen decreases tight junction protein ZO-1 expression in human primary gut tissues. Clin Immunol. 2017;183:174-180.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Ibrahim MA. Evaluation of metformin treatment effect on the levels of vaspin, zonulin and other biochemical parameters in polycystic ovary syndrome patients [Thesis]. Iraq: Tikrit University, 2020;218.
- Moreno-Navarrete JM, Sabater M, Ortega F, Ricart W, Fernandez-Real JM. Circulating zonulin, a marker of intestinal permeability, is increased in association with obesity-associated insulin resistance. PloSOne. 2012;7(5):e37160.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Zhou Z, Bian C, Luo Z, Guille C, Ogunrinde E, Wu J, et al. Progesterone decreases gut permeability through upregulating occludin expression in primary human gut tissues and Caco-2 cells. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1-3.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
- Ahmadi S, Razazan A, Nagpal R, Jain S, Wang BO, Mishra SP, et al. Metformin reduces aging-related leaky gut and improves cognitive function by beneficially modulating gut microbiome/goblet cell/mucin axis. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020;75(7):e9-e21.
[CrossRef], [GoogleScholar], [Pubmed]
Citation: Ibrahim MA (2022) Possible Relationship between Zonulin, Metformin and Insulin Resistance in Polycystic Ovarian Women. Adv Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 11:265.
Copyright: © 2022 Ibrahim MA. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.

