Indexed In
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
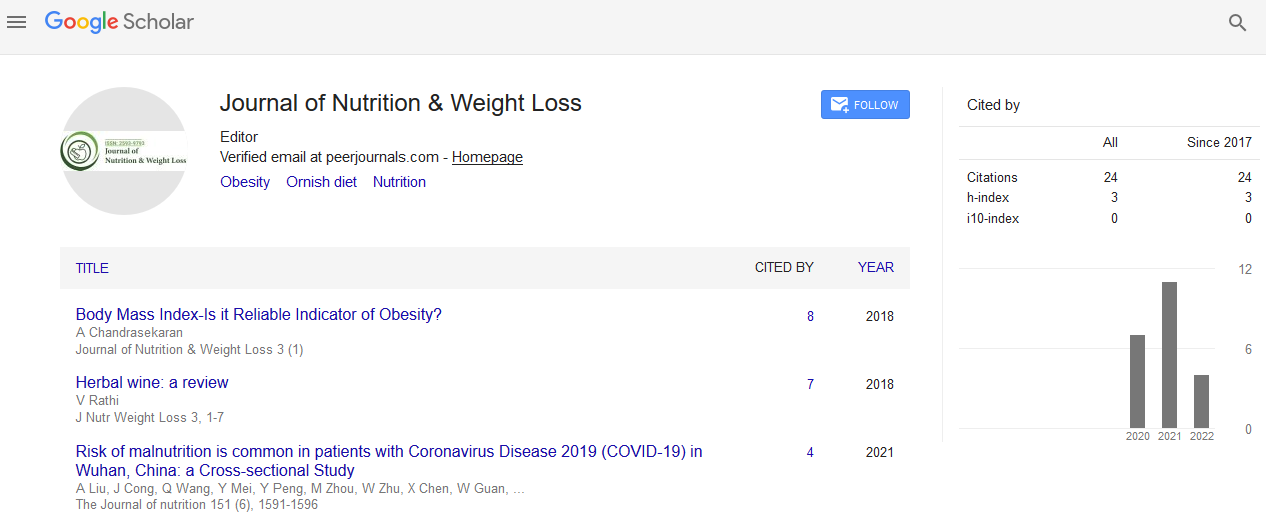
Perspective - (2023) Volume 8, Issue 2
Impact of Caloric Deficiency in Weight Management
Rosa Lopez*Received: 15-May-2023, Manuscript No. JNWL-23-22285; Editor assigned: 17-May-2023, Pre QC No. JNWL-23-22285 (PQ); Reviewed: 31-May-2023, QC No. JNWL-23-22285; Revised: 07-Jun-2023, Manuscript No. JNWL-23-22285 (R); Published: 14-Aug-2023, DOI: 10.35248/2593-9793.23.8.174
Description
In the realm of weight management, the concept of a caloric deficit has emerged as a fundamental strategy. This state, characterized by burning more calories than one consumes, is often employed as a method for weight loss. The human body requires a certain amount of energy (calories) each day to maintain its functions. This energy is derived from the food and beverages we consume. When the energy consumed matches the energy expended, we maintain our weight. However, when the energy consumed is less than the energy expended, a caloric deficit occurs, leading to weight loss.
Creating a caloric deficit can be achieved in two ways: reducing caloric intake or increasing physical activity. Reducing caloric intake involves modifying one’s diet to consume fewer calories. This could mean opting for lower-calorie foods, reducing portion sizes, or eliminating high-calorie, low-nutrient foods. On the other hand, increasing physical activity involves engaging in exercises that burn more calories, thereby increasing the total amount of energy expended. While the concept of a caloric deficit seems straightforward, it requires careful planning and execution. It’s important to ensure that the caloric deficit is achieved in a healthy and sustainable manner. Extreme caloric deficits can lead to nutrient deficiencies, loss of muscle mass, and other health complications. Therefore, it’s recommended to aim for a modest caloric deficit that can lead to steady and sustainable weight loss.
The quality of the calories consumed matters as much as the quantity. Consuming nutrient-dense foods can provide the body with the necessary vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients it needs to function optimally, even in a state of caloric deficit. Creating a caloric deficit can be accomplished through two primary methods: decreasing the number of calories consumed or increasing the amount of calories burned through physical activity. Decreasing caloric intake can involve making dietary modifications such as choosing foods with lower calorie content, reducing portion sizes, or avoiding foods that are high in calories but low in nutrients. Conversely, increasing physical activity can involve participating in exercises that burn a higher number of calories, which in turn increases the total amount of energy expended.
In addition to these basic strategies, it’s important to consider the role of macronutrients in weight loss. For instance, protein has been shown to be particularly beneficial during periods of caloric deficit. A diet that includes adequate protein can enhance weight loss and improve body composition. This is because protein can help preserve muscle mass while promoting fat loss, which is essential for maintaining metabolic rate during weight loss. Furthermore, it’s worth noting that the body’s response to a caloric deficit can vary among individuals. This underscores the importance of personalized weight loss strategies that take into account individual differences in metabolic responses.
In conclusion, a caloric deficit is a powerful tool for weight management. However, it should be approached with care, ensuring that the body receives adequate nutrition while losing weight. As always, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before embarking on a weight loss plan involving a caloric deficit. They can provide personalized advice based on our specific needs and goals, ensuring a safe and effective weight loss journey.
Citation: Lopez R (2023) Impact of Caloric Deficiency in Weight Management. J Nutr Weight Loss. 8:174.
Copyright: © 2023 Lopez R. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.