Indexed In
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Euro Pub
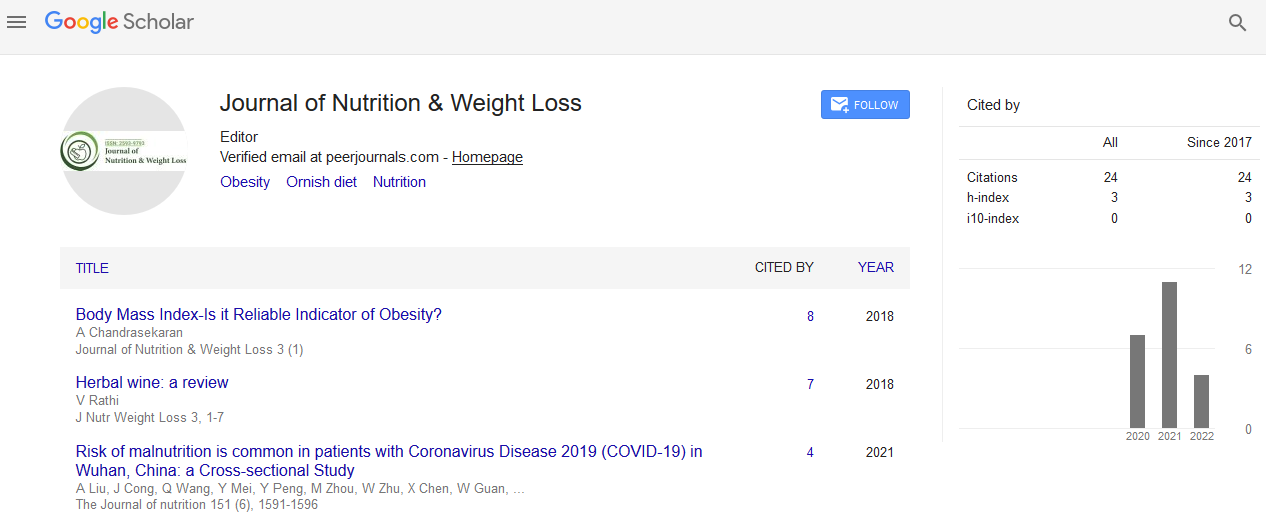
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Opinion Article - (2024) Volume 9, Issue 2
Comparative Study of Plant Based and Animal Based Diets on Weight Loss
James Garcia*Received: 29-May-2024, Manuscript No. JNWL-24-27985; Editor assigned: 12-Mar-0024, Pre QC No. JNWL-24-27985 (PQ); Reviewed: 14-Jun-2024, QC No. JNWL-24-27985; Revised: 21-Jun-2024, Manuscript No. JNWL-24-27985 (R); Published: 28-Jun-2024, DOI: 10.35248/2593-9793.24.9.210
Description
The comparative study of plant based and animal based diets on weight loss provides valuable insights into how different dietary approaches influence body composition and metabolic health. Both types of diets have unique characteristics that can impact weight management, depending on factors such as nutrient composition, caloric density and individual lifestyle preferences.
Plant-based diets, which highlight fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds and legumes, are typically high in dietary fiber, vitamins, minerals and antioxidants while being lower in saturated fats and calories. The high fiber content of plant based diets promotes satiety and helps regulate appetite by slowing gastric emptying and reducing hunger hormones. This can lead to a natural reduction in overall caloric intake without the need for deliberate calorie counting. Furthermore, plant based diets are associated with a lower dietary energy density, meaning they provide fewer calories per gram of food, allowing individuals to consume larger portions while maintaining a caloric deficit. This can be particularly advantageous for weight loss, as it supports sustained adherence to the diet.
Animal-based diets, on the other hand, often focus on protein rich foods such as meat, fish, eggs and dairy products. High protein diets have been shown to enhance satiety and support muscle preservation during weight loss. Protein’s thermogenic effect, or the energy required for digestion and metabolism, is higher than that of carbohydrates or fats, which can contribute to increased energy expenditure. Additionally, animal-based diets that emphasize lean protein sources may help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce cravings, making them effective for short term weight loss.
While both diets can lead to weight loss, differences in their long-term sustainability and health effects must be considered. Plant based diets have been associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes and certain cancers. Their emphasis on whole, nutrient-dense foods aligns with broader health goals beyond weight loss. However, individuals following a strictly plant based diet must ensure they consume adequate protein, vitamin B12, iron and omega-3 fatty acids, which are more readily available in animal based foods.
Animal based diets, particularly those that include high amounts of red and processed meats, have been linked to adverse health outcomes such as increased risks of cardiovascular disease and colorectal cancer. Therefore, choosing lean and minimally processed protein sources is important when adopting an animal based approach. Moreover, animal based diets tend to be lower in fiber, which may impact gut health and long-term satiety compared to plant based options.
Cultural, ethical and environmental considerations also play a role in the choice between plant-based and animal based diets. Plant based diets are generally more sustainable and environmentally friendly, requiring fewer natural resources and producing lower greenhouse gas emissions. This aspect has prompted many individuals to adopt plant-based eating patterns not only for personal health but also for environmental and ethical reasons.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of plant based vs. animal based diets for weight loss depends on individual preferences, dietary habits and health goals. A balanced approach that incorporates elements of both diets, such as a flexitarian or Mediterraneanstyle eating pattern, may provide the best of both worlds. These approaches emphasize plant based foods while allowing moderate consumption of high quality animal based proteins, providing a diverse range of nutrients and making the diet easier to sustain over time.
In conclusion, both plant based and animal based diets have their own advantages and challenges when it comes to weight loss. Plant based diets excel in promoting satiety and providing broader health benefits, while animal based diets are effective in enhancing protein intake and preserving lean body mass. Personalization and a focus on nutrient-dense, minimally processed foods are key to achieving successful and sustainable weight loss, regardless of the dietary approach chosen.
Citation: Garcia J (2024). Comparative Study of Plant Based and Animal Based Diets on Weight Loss. J Nutr Weight Loss. 9:210.
Copyright: © 2024 Garcia J. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.