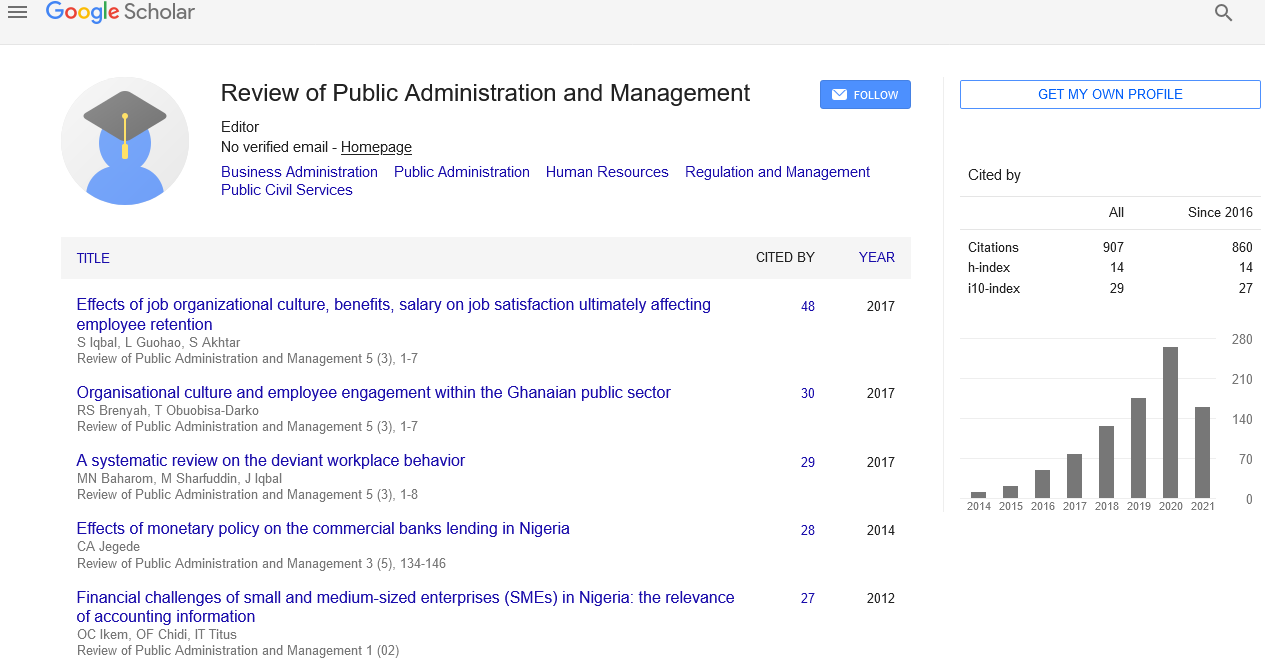
Indexed In
- CiteFactor
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Scholarsteer
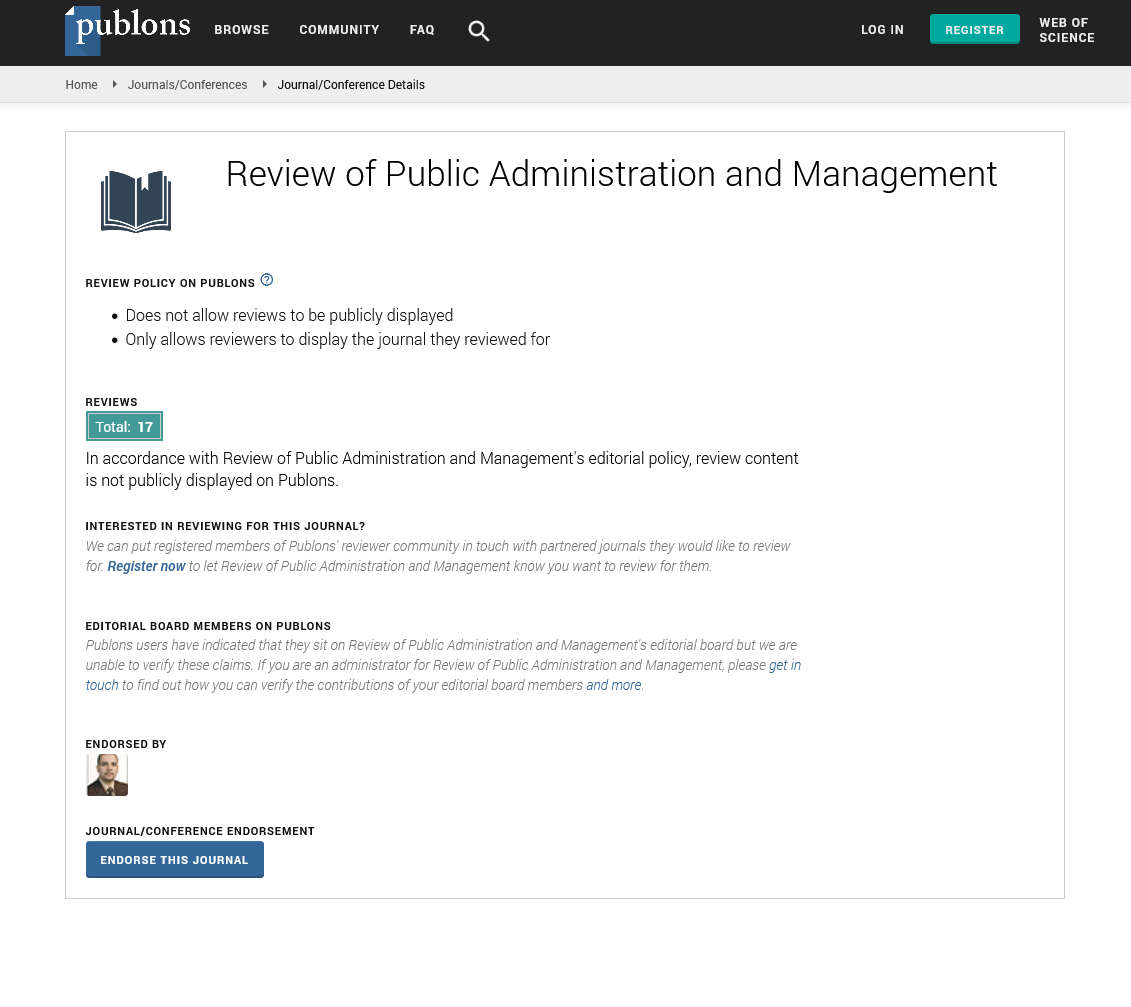
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Opinion Article - (2024) Volume 12, Issue 1
Challenges and Risks in Inter-Organizational Collaborations and Managing Financial Resources with Control Mechanism
Mona Luica*Received: 01-Mar-2024, Manuscript No. RPAM-24-25531; Editor assigned: 04-Mar-2024, Pre QC No. RPAM-24-25531 (PQ); Reviewed: 18-Mar-2024, QC No. RPAM-24-25531; Revised: 25-Mar-2024, Manuscript No. RPAM-24-25531 (R); Published: 01-Apr-2024, DOI: 10.35248/2315-7844.24.12.446
Description
Inter-organizational collaborations have become increasingly prevalent in the public sector as governments seek to address complex challenges that transcend organizational boundaries. These collaborations involve multiple organizations working together to achieve common goals, such as delivering public services, implementing policy initiatives, or addressing community needs. However, ensuring effective coordination and alignment of efforts in such collaborations can be challenging. Control mechanisms play a critical role in managing these collaborations, ensuring accountability, transparency, and the achievement of desired outcomes. Inter-organizational collaborations involve the pooling of resources, expertise, and capabilities across multiple organizations to achieve shared objectives. These collaborations may take various forms, including partnerships, networks, alliances, and consortia. In the public sector, inter-organizational collaborations are often formed to address complex issues that require a collective response, such as public health emergencies, environmental conservation, or economic development initiatives. Collaboration allows organizations to leverage complementary strengths, share risks and responsibilities, and achieve greater impact than they could individually. While inter-organizational collaborations offer numerous benefits, they also pose challenges related to coordination, communication, and accountability. Control mechanisms are essential for managing these collaborations effectively, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently, risks are mitigated, and objectives are achieved. Control mechanisms provide a framework for the behavior of participating organizations, clarifying roles and responsibilities, and monitoring performance. By establishing clear rules, processes, and incentives, control mechanisms promote trust, collaboration, and alignment of interests among collaborating organizations.
Contracts and legal agreements are fundamental control mechanisms used in inter-organizational collaborations to formalize the terms and conditions of the partnership. These documents outline the rights, obligations, and expectations of participating organizations, including roles, responsibilities, resource contributions, and decision-making processes. Contracts may also include provisions for dispute resolution, termination clauses, and intellectual property rights, ensuring clarity and legal enforceability. Governance structures define the decision-making processes, authority relationships, and accountability mechanisms within inter-organizational collaborations. These structures may include governing boards, steering committees, or advisory councils composed of representatives from participating organizations. Governance bodies oversee the strategic direction, resource allocation, and performance monitoring of the collaboration, ensuring that decisions are made collectively and aligned with organizational objectives. Performance metrics and reporting mechanisms are used to monitor and evaluate the progress and outcomes of inter-organizational collaborations. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are established to measure the effectiveness, efficiency, and impact of collaborative efforts against predefined goals and benchmarks. Regular reporting requirements ensure transparency, accountability, and information sharing among participating organizations, enabling timely feedback and course corrections as needed.
Financial controls are essential for managing the financial resources allocated to inter-organizational collaborations and ensuring accountability for their use. Financial controls may include budgetary oversight, expenditure tracking, and auditing procedures to monitor the use of funds and prevent fraud, waste, and abuse. Participating organizations may be required to adhere to financial reporting standards, procurement guidelines, and internal control procedures to maintain transparency and integrity in financial management. Control mechanisms clarify roles, responsibilities, and expectations, ensuring that participating organizations are held accountable for their contributions and performance. Control mechanisms facilitate coordination and communication among collaborating organizations, reducing duplication of efforts, and promoting synergy. Control mechanisms help identify and mitigate risks associated with inter-organizational collaborations, ensuring that potential issues are addressed proactively. Control mechanisms promote transparency and information sharing, enabling stakeholders to monitor progress, measure performance, and make informed decisions. Ensuring coordination and alignment of efforts among diverse organizations with different priorities, cultures, and operating procedures can be challenging. Control mechanisms may be influenced by power dynamics and imbalances among participating organizations, leading to conflicts of interest and governance issues. Compliance with control mechanisms may impose administrative burdens and costs on participating organizations, particularly smaller entities with limited resources. Balancing the need for control and accountability with the flexibility and autonomy required for innovation and adaptation in inter-organizational collaborations.
Control mechanisms play a essential role in managing inter-organizational collaborations within public administration, ensuring accountability, transparency, and the achievement of desired outcomes. By establishing clear rules, governance structures, performance metrics, and financial controls, collaborating organizations can mitigate risks, enhance coordination, and maximize the impact of their efforts. However, implementing control mechanisms requires careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and ongoing monitoring to address challenges and ensure effectiveness. As governments continue to rely on inter-organizational collaborations to address complex challenges, the importance of effective control mechanisms in promoting successful outcomes cannot be overstated.
Citation: Luica M (2024) Challenges and Risks in Inter-Organizational Collaborations and Managing Financial Resources with Control Mechanism. Review Pub Administration Manag. 12:446.
Copyright: © 2024 Luica M. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.