Indexed In
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- ResearchBible
- Electronic Journals Library
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- SWB online catalog
- Virtual Library of Biology (vifabio)
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Short Communication - (2019) Volume 8, Issue 1
4-Hexylresorcinol a New Molecule for Cosmetic Application
Fidalgo J, Deglesne PA, Arroya R, Ranneva E and Deprez P*Received: 08-Feb-2019 Published: 20-Mar-2019, DOI: 10.35248/2167-7956.19.8.170
Abstract
4-hexylresorcinol is the most studied and well known alkylresorcinol derivative, known for its pharmacological properties as anesthetic, antiseptic and anthelmintic. It can be both applied topically in creams and included as an active ingredient in throat lozenges. Its interest as a cosmetic ingredient is more recent and is increasing owing to its anti-oxidant, anti-glycation and melanogenic inhibitory properties and that it is safe to use. All those elements make 4-hexylresorcinol a cosmetic ingredient of choice for skin care products. This short review summarizes its mechanism of action and some evidences of its efficacy in certain biological processes of interest in skincare.
Keywords
4-hexylresorcinol; Pigmentation; Photoaging; Oxidative stress; Glycation
What is 4-hexylresorcinol?
4-hexylresorcinol (4-Hexyl-1,3-benzenediol; 4-HR) is an alkylresorcinol (AR) with 6 methylenes in length at fourth position included in the list of drugs in the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1999 (Figure 1). It is an organic amphiphilic compound that mimics the tyrosinase natural substrate, tyrosine. It is an analog of resorcinol, a compound used as an antiseptic and disinfectant in topical use [1]. It has amphiphilic properties, possessing a hydrophilic moiety and a hydrophophic moiety (highlighted in green circle in its structure Figure 2). This amphiphilic character makes 4-HR able to interact with the phospholipid bilayers of biological membranes while its hydrophilic moiety makes it possible to share a proton in aqueous media [2,3]. Furthermore, 4-HR has a GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) status, being considered safe and also effective as an anti-browning agent in food applications [4].
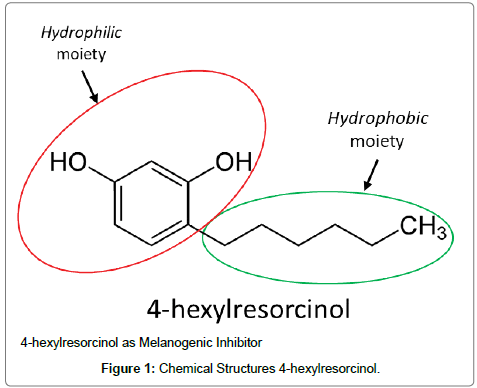
Figure 1: Chemical Structures 4-hexylresorcinol.
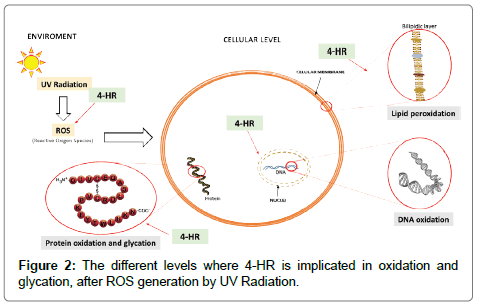
Figure 2: The different levels where 4-HR is implicated in oxidation and glycation, after ROS generation by UV Radiation.
4-Hexylresorcinol as Melanogenic Inhibitor
The melanin synthesis is an important biological process of pigmentation of the skin. Melanogenesis is influenced by the solar radiation which increases the synthesis of melanin pigments (eumelanin and pheomelanin). The synthesis of melanin starts from the conversion of L-tyrosine into L-DOPA followed by the conversion of the latter to DOPAquinone by the tyrosinase enzyme. Tyrosinase converts L-tyrosine into L-DOPA and L-DOPA into DOPAquinone by its monophenolase and diphenolase activities, respectively. Then, a series of enzymatic reactions further convert the DOPAquinone intermediate in the different human skin melanin pigments. 4-HR resorcinol potently inhibits both monophenolase and diphenolase activities of mushroom tyrosinase [5,6]. It is thought that 4-HR binds to tyrosinase directly by competing with its natural substrate, L-tyrosine, and blocking its enzymatic activity [7]. Interestingly 4-HR was demonstrated to be more potent inhibitor of tyrosinase for both tyrosine substrates (L-tyrosine and L-DOPA) than hydroquinone, kojik acid or licorice extract (Table 1) [8-10].
| Compound | IC50 (µM) Mushroom tyrosinase |
|---|---|
| 4-Hexylresorcinol | 1.2 [7] |
| Hydroquinone | 26 [7] |
| Kojic acid | 300 [8] |
Table 1: Potency (IC50) values (µM) of 4-hexylresorcinol, hydroquinone and kojik acid on inhibiting mushroom tyrosinase activity.
4-Hexylresorcinol as Antioxidant
Oxidative stress in skin plays a major role in the aging process. This is true for intrinsic aging and even more for extrinsic aging. Although the results are quite different in dermis and epidermis, extrinsic aging is driven to a large extent by oxidative stress caused by solar light including Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation. UV radiations are known to induce Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) at the cellular level leading to cellular oxidative stress [3,11-13]. Skin cells suffering oxidative stress activates to a certain level the antioxidant machinery comprising Glutathione (GSH) that protects cells from oxidative damage as well as some primary antioxidant enzymes, such as Glutathione Peroxidase (GPX) and Glutathione Reductase (GR) [14,15]. It has been proven in DNA damage models in human lymphocytes induced by H2O2 that 4-HR administration increased GSH levels but also GPX and GR activities, limiting subsequently oxidative stress and DNA damage [16]. As a phenol derivative, 4-HR, can also donate a proton to free radicals by means of its phenolic hydrogen allowing it to scavenge both peroxyl radical and oxygen superoxide and reduce peroxidation of lipids [2,17,18]. Finally, reactive oxygen species may also lead to oxidation reactions of proteins [19]. Due to its amphiphilic character and hydrophilic moiety, 4-HR is able to interact with both with lipids and proteins to efficiently reduce their oxidation [2,3].
4-Hexylresorcinol as a Non-Enzymatic Glycosylation Inhibitor
Glycation is considered together with oxidative stress as one of the key factors in skin aging [18]. Glycation resulting from the nonenzymatic addition of sugars to proteins generates abnormal protein cross-linking or protein adducts between adjacent proteins in the skin. Glycation leads to the formation of products called Advanced Glycation End-Products (AGEs) which can be formed either intra- or extracellularly [20]. The glycation reaction results from a non-enzymatic reaction between a sugar and a free amine group of Lysine, Arginine amino acids of proteins. Maillard reaction is one of the reactions that take place during the process of non-enzymatic glycation of proteins. 4-HR was found in vitro to inhibit the formation of Maillard reaction products [21]. Moreover, since glycation is linked to ROS production [22,23] antioxidant activity of 4-HR could also limit the formation of abnormal cross-linking of proteins.
Anti-inflammatory Effects of 4-HR
Inflammation is a complex physiological process, where the transcription factor NF-kB (Nuclear Factor-Kappa Beta) has been documented to play an important role in the inflammatory response [24,25]. NF-kB is activated by numerous pro-inflammatory stimuli. ROS triggers NF-κB, which in the canonical pathway is activated by IkB kinase (IKK) and translocate to the nuclei upregulating the expression of inflammatory mediators, such as iNOS, COX-2 and cytokines like TNF-α and IL-1ß leading to inflammation [26]. Natural phenolic compounds have been considered as NF-kB inhibitors [27] and alkylresorcinols (including 4-HR) have demonstrated to have an antiinflammatory effect [26]. Recently, 4-HR has been reported to inhibit NF-kB phosphorylation in vitro while in different studies, the ability of inhibiting NF-kB of 4-HR was related with an increased expression of ECM (extra cellular matrix) proteins in vitro in human’s fibroblast, with a significant clinical improvement in photo damaged skin [28,29].
Conclusion
Due to its anti-oxidant, melanogenic and glycation inhibitory properties, 4-hexylresorcinol is a promising molecule for cosmetic/ aesthetic application including the treatment of hyperpigmentated disorder and photo-aging.
REFERENCES
- Chaudhuri RK. Hexylresorcinol: providing skin benefits by modulating multiple molecular targets. Cosmeceut & Act Cos. 2015;3:71-82.
- Kozubek A, Tyman JHP. Resorcinolic lipids, the natural nonisoprenoid phenolic amphiphiles and their biologic activity. Chem Rev. 1999;99:1-25.
- Stasiuk M, Kozubek A. Biological activity of phenolic lipids. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010;67:841-860.
- Radha I, Craig W, Bohmont RJM. 4-Hexylresorcinol and prevention of shrimp blackspot: Residual analyses. J Food Comp Anal. 1991;4:148-157.
- Chen Q-X, Ke L-N, Song K-K, Huang H. Inhibitory Effects of Hexylresorcinol and Dodecylresorcinol on Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) Tyrosinase. Protein J. 2004;23:135-141.
- Dawley RM, Flurkey WH. 4-Hexylresorcinol, a Potent Inhibitor of Mushroom Tyrosinase. J Food Sci. 1993;58: 609-610.
- Arias E, González J, Peiró JM, Oria R, Lopez-Buesa P. Browning prevention by ascorbic acid and 4-hexylresorcinol: different mechanisms of action on polyphenol oxidase in the presence and in the absence of substrates. J Food Sci. 2007;72:C464-C470.
- Chaudhuri RK. Effective skin lightening with protective property. Pers Care. 2010;39-44.
- Neeley E, Fritch G, Fuller A, Wolfe J. Variations in IC50 Values with Purity of Mushroom Tyrosinase. Int J Mol Sci. 2009;10:3811-3823.
- Mann T, Gerwat W, Batzer J, Eggers K. Inhibition of Human Tyrosinase Requires Molecular Motifs Distinctively Different from Mushroom Tyrosinase. J Investig Dermat. 2018;138:1601-1608.
- Kuse Y, Ogawa K, Tsuruma K, Shimazawa M. Damage of photoreceptor-derived cells in culture induced by light emitting diode-derived blue light. Sci Rep. 2014;4: 5223.
- Liebel F, Kaur S, Ruvolo E, Kollias N. Irradiation of Skin with Visible Light Induces Reactive Oxygen Species and Matrix-Degrading Enzymes. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:1901-1907.
- Nimse SB, Pal D. Free radicals, natural antioxidants, and their reaction mechanisms. RSC Adv. 2015;5:27986-28006.
- Pompella A, Visvikis A, Paolicchi A, De Tata V, Casini AF. The changing faces of glutathione, a cellular protagonista. Biohem Pharmacol. 2003;66:1499-1503.
- Ahmad S. Antioxidant Mechanisms of Enzymes and Proteins. Oxid Stress & Antioxidant Defense. 1995;7:238-272.
- Yen GC, Duh PD, Lin CW. Effects of resveratrol and 4-hexylresorcinol on hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative DNA damage in human lymphocytes. Free Rad Res. 2003;37:509-514.
- Kamal-Eldin A, Pouru A, Eliasson C, Åman P. Alkylresorcinols as antioxidants: Hydrogen donation and peroxyl radical-scavenging effects. J Sci Food Agric. 2000; 81:353-356.
- Gryazeva IV, Davydova OK, Deryabin DG. Evaluation of the potential of alkylresorciniols as superoxide anion scavengers and soxregulon modulators using nitroblue tetrazolium and bioluminiscent cell-based assays. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2015;20:24-37.
- Zhang W, Xiao S, Ahn DU. Protein oxidation: basic principles and implications for meat quality. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2013;53:1191- 1201.
- Gkogkolou P, Böhm M. Advanced glycation end products. Key players in skin aging. Dermatoendocrinol. 2012;4:259-270.
- Cheriot SC, Billaud C, Nicolas J. Use of experimental design methodology to prepare Maillard reaction products from glucose and cysteine inhibitors of polyphenol oxidase from eggplant (Solanum melongena). J Agric Food Chem. 2006;54:5120-5126.
- Schmid D, Muggli R, Zülli Fred, Mibelle AG. Collagen glycation and skin aging. Mibelle Biochemistry Publication Cosmetics. 2002;1-6.
- Pageon H. Reaction of glycation and human skin: The effects on the skin and its components, reconstructed skin as a model. Pathologie Biologie. 2010;58:226-231.
- Lawrence T. The Nuclear Factor NF-kB Pathway in Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Bio. 2009;l 1: a001651.
- Li X. NF-kappaB-dependent signaling pathways. Exp Hematol. 2002;30:285-296.
- Gliwa J. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of alkylresorcinols from rye bran. Carleton University Canada. 2003;20:1-6.
- Nam NH. Naturally Occurring NF-kB Inhibitors. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2006;8:945-951.
- Kim SG, Lee SW, Park YW, Jeong JH. 4-hexylresorcinol inhibits NF- κB phosphorylation and has a synergistic effect with cisplatin in KB cells. Oncol Rep. 2011;26:1527-1532.
- Kaur S, Kizoulis M, Fantasia J, Oddos T, Bigot N. 4-Hexyl-1,3- phenylenediol, a nuclear factor-κB inhibitor, improves photodamaged skin and clinical signs of ageing in a double-blinded, randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:218-226.
Citation: Deprez P (2019) 4-Hexylresorcinol a New Molecule for Cosmetic Application. J Biomol Res Ther, 8: 170. doi: 10.35248/2167-7956.19.8.170
Copyright: © 2019 Deprez P, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the term of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

